Cats, with their serene and comforting presence, contribute significantly to creating a nurturing and warm atmosphere in homes. They not only bring joy and companionship but also enhance the emotional well-being of their owners. However, the responsibility of owning a cat involves more than providing love and shelter; it requires a dedicated approach to maintaining their health. Cardiovascular diseases in cats, though not rare, demand particular attention due to their potential to impact a cat’s health and lifespan severely.
Understanding Cardiovascular Disease in Cats
Cardiovascular disease in cats encompasses a broad spectrum of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, which can lead to diminished cardiac function and serious health implications. These conditions may be either congenital, meaning present from birth, or acquired throughout the cat’s life due to various factors such as diet, activity level, or underlying health issues. Proper understanding and timely management of these diseases are crucial for ensuring the long-term health and quality of life of affected felines.
Diagnostic Techniques for Identifying Heart Disease in Cats
Accurate diagnosis is critical for effective management of heart disease in cats. Veterinarians typically employ several diagnostic methods:
– Chest Radiography: X-rays of the chest provide valuable information about the size and shape of the heart, the state of the lung tissue, and the presence of any fluid around the heart or lungs.
– Electrocardiography (ECG): This test measures the electrical activity of the heart, providing insights into heart rhythm and rate, which are crucial for diagnosing various types of heart disease.
– Echocardiography: A non-invasive ultrasound test that creates detailed images of the heart, allowing vets to assess the motion of the heart’s walls and valves, blood flow, and overall heart function.
– Clinical and Biochemical Blood Tests: These tests help detect other conditions that might affect the heart or be affected by heart disease, such as kidney function or thyroid disease.
– Tonometry: Although primarily used to measure eye pressure, tonometry can also provide indirect assessments of blood pressure, which is important in the diagnosis of hypertension, a common comorbidity in cardiac patients.
Recognizing Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease in Cats
The clinical presentation of heart disease in cats can be subtle or overt, and symptoms often worsen as the disease progresses. Key indicators include:
– Reduced Activity and Lethargy: Cats may become less interested in play and seem tired more quickly.
– Respiratory Distress: Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing can occur, especially after exercise.
– Appetite Changes and Weight Loss: Cats might lose weight due to decreased appetite.
– Physical Changes: Pale or bluish gums, fluid retention leading to swelling, or a noticeable drop in body temperature.
– Neurological Issues: Including seizures or problems with coordination, indicating advanced disease.
These symptoms warrant immediate veterinary consultation to prevent further deterioration of the cat’s health.
Classification of Cardiovascular Diseases in Cats
Cardiovascular conditions in cats are generally divided into:
Congenital Heart Defects
– Aortic and Pulmonary Stenosis: Narrowing of the major arteries coming from the heart, which can lead to increased cardiac workload.
– Septal Defects: Abnormal openings in the heart walls that allow blood to flow between the chambers improperly.
– Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A condition where a fetal blood vessel fails to close after birth, affecting normal blood circulation.
Acquired Heart Diseases
– Cardiomyopathies: These are diseases of the heart muscle that affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
– Infective Endocarditis: An infection of the heart valves that can damage cardiac tissue.
– Pericardial Disease: Conditions affecting the outer membrane enclosing the heart.
– Hypertension and Thromboembolisms: High blood pressure and blood clots that can lead to severe complications like stroke or heart failure.
Treatment Options for Heart Disease in Cats
Managing heart disease in cats might involve:
– Medication: To improve heart function, control rhythm disturbances, reduce fluid accumulation, and prevent blood clots.
– Dietary Management: Special cardiac diets can help manage heart disease by controlling factors like sodium intake.
– Regular Monitoring: Frequent check-ups to adjust treatment as the disease progresses or improves.
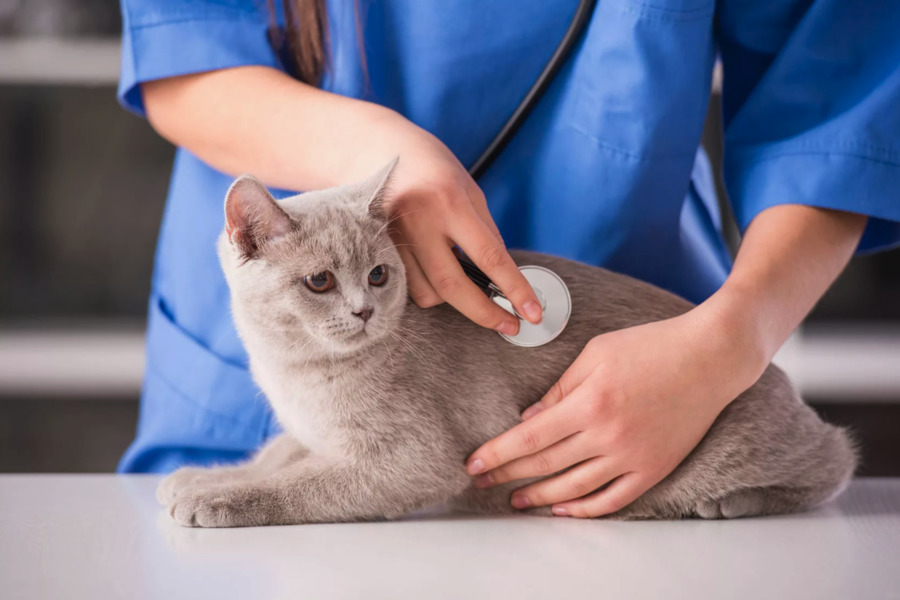

Preventive Measures for Heart Health in Cats
Prevention of heart disease involves:
– Regular Veterinary Visits: Early detection through routine exams can greatly impact the management of heart disease.
– Lifestyle Management: Keeping cats active and at a healthy weight helps mitigate the risk of heart disease.
– Stress Reduction: Creating a calm environment to avoid stress-related complications.
– Nutritional Care: Ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall heart health.
Vets in the City: Premier Heart Care for Cats in Dubai
Vets in the City offer exceptional cardiac care with advanced diagnostic tools and treatments staffed by experienced veterinarians. Vets in the City- best pet clinic in Dubai. Their commitment to pet health is reflected in their comprehensive approach to diagnosing and managing cardiovascular diseases, ensuring that cats receive the best possible care to maintain a healthy and active life.
Through diligent care and regular veterinary oversight, the challenges of cardiovascular disease in cats can be managed effectively, allowing these cherished pets to lead fuller, healthier lives.

Snowboarder, follower of Christ, music blogger, hand letterer and AIGA member. Acting at the crossroads of simplicity and sustainability to give life to your brand. Let’s chat.


